What You Need to Know About Low Back Pain (LBP)
What You Need to Know About Low Back Pain (LBP)- by Brian Tovin, PT, DPT, MMSc, SCS, ATC, FAAOMPT
1. What are the typical causes of musculoskeletal LBP?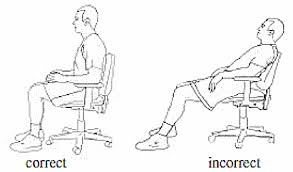
- Trauma: from an accident or lifting incorrectly can result in soft tissue damage to the muscles, ligaments, or discs.
- Poor Posture: poor sitting postures over a prolonged period of time can lead to problems with muscles, ligaments and discs.
- Muscle Imbalances: weak or tight muscles can lead to excessive stress on the soft tissue
2. Do I need to know the exact structure that is causing my pain in order to have successful physical therapy treatment? 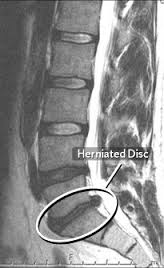
-NO! An MRI may show if someone has a disc bulge. However, research has demonstrated that over 70% of people over 40 years old will have a disc bulge on MRI…EVEN IF THEY HAVE NO SYMPTOMS.
-Diagnostic testing for LBP is more important to tell the healthcare practitioner what is NOT causing the pain (ie. Fracture, cancer, etc) vs what is causing the pain.
-Once physical therapists know that the origin of the pain is musculoskeletal, we will assess the impairments (ie. Muscle weakness, muscle tightness, trigger points, decreased joint mobility or instability) to make the best clinical decisions in planning a treatment program. 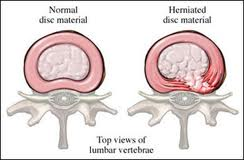
3. How do I know if my LBP will respond to physical therapy?
– While the majority of patients who present with LBP are appropriate for physical therapy, sometimes other structures (such as organs) or conditions (ie. cancer) can refer symptoms to the low back region and may not respond to physical therapy.
– Non-musculoskeletal causes of LBP can be very serious and need to be ruled out by a healthcare professional.
– Here are the “red flag” questions that need to be considered; if more than one of these things occurs, you should see an MD immediately:
1) Is the pain present all the time (there are no positions or time of day that changes the pain level)?
2) Is the pain the worst at night?
3) Do you experience night sweats, fevers, or chills?
4) Has there been a recent loss or gain of weight?
4. Are there any other signs or symptoms that suggest I see a Physician immediately?
Even musculoskeletal causes of LBP can be serious and warrant an immediate evaluation. Some of these signs include:
- Unbearable pain that has lasted more than a few days
- Weakness in the lower extremities, especially foot drop (inability to lift the toes up while walking)
- Loss of sensation in the groin or saddle (genital) area structures
- Experienced changes in your bowel or bladder function
5. What are some of the effective treatments that a physical therapist can offer for patients with LBP: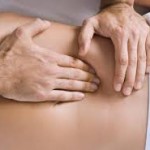
- Manual therapy: which includes soft tissue mobilization, joint manipulation, stretching techniques, trigger point dry needling
- Therapeutic Exercises: used to improve strength, mobility, flexibility, and stability
- Modalities: Ultrasound, electrical stimulation, Laser, traction
- Education: To prevent recurrence
Come see the experts at the Sports Rehabilitation Center for your care!
While some healthcare practitioners will focus on one type of treatment (ie. Adjustments or stabilization), the most effective treatment program will be individualized to meet the needs of a specific patient. The staff at The Sports Rehabilitation Center will provide a detailed evaluation to determine the best course of treatment to get you back to normal as quickly and safely as possible.